# optuna
**Repository Path**: gongchengqi/optuna
## Basic Information
- **Project Name**: optuna
- **Description**: No description available
- **Primary Language**: Unknown
- **License**: MIT
- **Default Branch**: master
- **Homepage**: None
- **GVP Project**: No
## Statistics
- **Stars**: 1
- **Forks**: 1
- **Created**: 2024-03-08
- **Last Updated**: 2024-06-26
## Categories & Tags
**Categories**: Uncategorized
**Tags**: None
## README

Sample code with scikit-learn
[](http://colab.research.google.com/github/optuna/optuna-examples/blob/main/quickstart.ipynb)
```python
import ...
# Define an objective function to be minimized.
def objective(trial):
# Invoke suggest methods of a Trial object to generate hyperparameters.
regressor_name = trial.suggest_categorical('regressor', ['SVR', 'RandomForest'])
if regressor_name == 'SVR':
svr_c = trial.suggest_float('svr_c', 1e-10, 1e10, log=True)
regressor_obj = sklearn.svm.SVR(C=svr_c)
else:
rf_max_depth = trial.suggest_int('rf_max_depth', 2, 32)
regressor_obj = sklearn.ensemble.RandomForestRegressor(max_depth=rf_max_depth)
X, y = sklearn.datasets.fetch_california_housing(return_X_y=True)
X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val = sklearn.model_selection.train_test_split(X, y, random_state=0)
regressor_obj.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = regressor_obj.predict(X_val)
error = sklearn.metrics.mean_squared_error(y_val, y_pred)
return error # An objective value linked with the Trial object.
study = optuna.create_study() # Create a new study.
study.optimize(objective, n_trials=100) # Invoke optimization of the objective function.
```
> [!NOTE]
> More examples can be found in [optuna/optuna-examples](https://github.com/optuna/optuna-examples).
>
> The examples cover diverse problem setups such as multi-objective optimization, constrained optimization, pruning, and distributed optimization.
## Installation
Optuna is available at [the Python Package Index](https://pypi.org/project/optuna/) and on [Anaconda Cloud](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/optuna).
```bash
# PyPI
$ pip install optuna
```
```bash
# Anaconda Cloud
$ conda install -c conda-forge optuna
```
> [!IMPORTANT]
> Optuna supports Python 3.7 or newer.
>
> Also, we provide Optuna docker images on [DockerHub](https://hub.docker.com/r/optuna/optuna).
## Integrations
Optuna has integration features with various third-party libraries. Integrations can be found in [optuna/optuna-integration](https://github.com/optuna/optuna-integration) and the document is available [here](https://optuna-integration.readthedocs.io/en/stable/index.html).
Supported integration libraries
* [Catalyst](https://github.com/optuna/optuna-examples/tree/main/pytorch/catalyst_simple.py)
* [Catboost](https://github.com/optuna/optuna-examples/tree/main/catboost/catboost_pruning.py)
* [Dask](https://github.com/optuna/optuna-examples/tree/main/dask/dask_simple.py)
* [fastai (v2)](https://github.com/optuna/optuna-examples/tree/main/fastai/fastaiv2_simple.py)
* [Keras](https://github.com/optuna/optuna-examples/tree/main/keras/keras_integration.py)
* [LightGBM](https://github.com/optuna/optuna-examples/tree/main/lightgbm/lightgbm_integration.py)
* [MLflow](https://github.com/optuna/optuna-examples/tree/main/mlflow/keras_mlflow.py)
* [MXNet](https://github.com/optuna/optuna-examples/tree/main/mxnet/mxnet_integration.py)
* [PyTorch](https://github.com/optuna/optuna-examples/tree/main/pytorch/pytorch_simple.py)
* [PyTorch Ignite](https://github.com/optuna/optuna-examples/tree/main/pytorch/pytorch_ignite_simple.py)
* [PyTorch Lightning](https://github.com/optuna/optuna-examples/tree/main/pytorch/pytorch_lightning_simple.py)
* [TensorBoard](https://github.com/optuna/optuna-examples/tree/main/tensorboard/tensorboard_simple.py)
* [TensorFlow](https://github.com/optuna/optuna-examples/tree/main/tensorflow/tensorflow_estimator_integration.py)
* [tf.keras](https://github.com/optuna/optuna-examples/tree/main/tfkeras/tfkeras_integration.py)
* [Weights & Biases](https://github.com/optuna/optuna-examples/tree/main/wandb/wandb_integration.py)
* [XGBoost](https://github.com/optuna/optuna-examples/tree/main/xgboost/xgboost_integration.py)
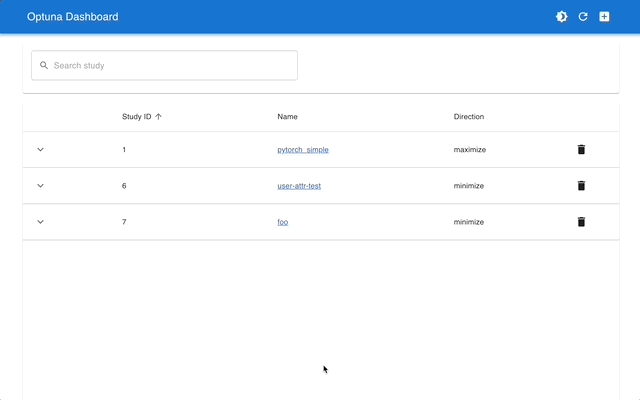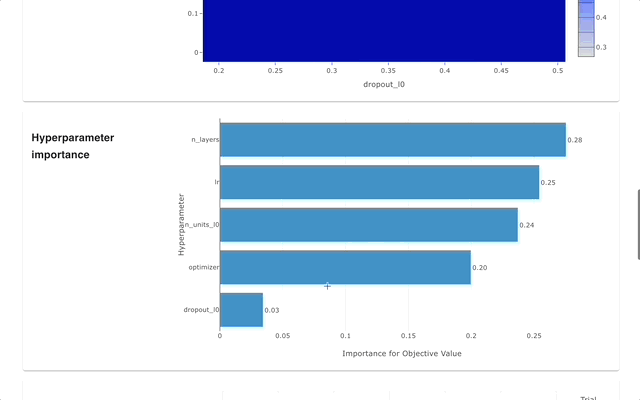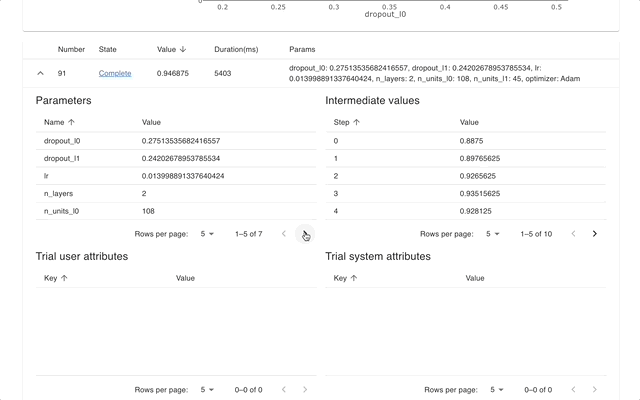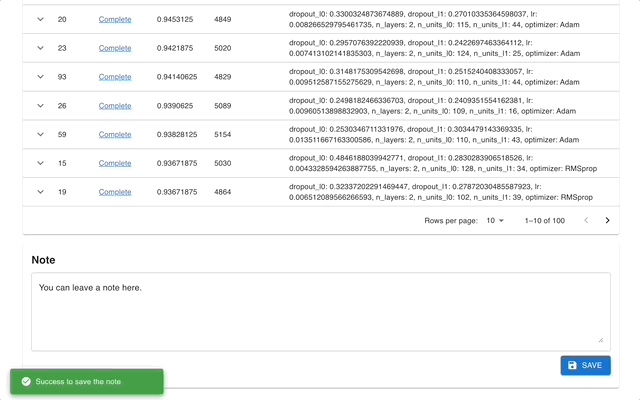
## Web Dashboard
[Optuna Dashboard](https://github.com/optuna/optuna-dashboard) is a real-time web dashboard for Optuna.
You can check the optimization history, hyperparameter importance, etc. in graphs and tables.
You don't need to create a Python script to call [Optuna's visualization](https://optuna.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/visualization/index.html) functions.
Feature requests and bug reports are welcome!
`optuna-dashboard` can be installed via pip:
```shell
$ pip install optuna-dashboard
```
> [!TIP]
> Please check out the convenience of Optuna Dashboard using the sample code below.
Sample code to launch Optuna Dashboard
Save the following code as `optimize_toy.py`.
```python
import optuna
def objective(trial):
x1 = trial.suggest_float("x1", -100, 100)
x2 = trial.suggest_float("x2", -100, 100)
return x1 ** 2 + 0.01 * x2 ** 2
study = optuna.create_study(storage="sqlite:///db.sqlite3") # Create a new study with database.
study.optimize(objective, n_trials=100)
```
Then try the commands below:
```shell
# Run the study specified above
$ python optimize_toy.py
# Launch the dashboard based on the storage `sqlite:///db.sqlite3`
$ optuna-dashboard sqlite:///db.sqlite3
...
Listening on http://localhost:8080/
Hit Ctrl-C to quit.
```
## Communication
- [GitHub Discussions] for questions.
- [GitHub Issues] for bug reports and feature requests.
[GitHub Discussions]: https://github.com/optuna/optuna/discussions
[GitHub issues]: https://github.com/optuna/optuna/issues
## Contribution
Any contributions to Optuna are more than welcome!
If you are new to Optuna, please check the [good first issues](https://github.com/optuna/optuna/labels/good%20first%20issue). They are relatively simple, well-defined, and often good starting points for you to get familiar with the contribution workflow and other developers.
If you already have contributed to Optuna, we recommend the other [contribution-welcome issues](https://github.com/optuna/optuna/labels/contribution-welcome).
For general guidelines on how to contribute to the project, take a look at [CONTRIBUTING.md](./CONTRIBUTING.md).
## Reference
If you use Optuna in one of your research projects, please cite [our KDD paper](https://doi.org/10.1145/3292500.3330701) "Optuna: A Next-generation Hyperparameter Optimization Framework":
BibTeX
```bibtex
@inproceedings{akiba2019optuna,
title={{O}ptuna: A Next-Generation Hyperparameter Optimization Framework},
author={Akiba, Takuya and Sano, Shotaro and Yanase, Toshihiko and Ohta, Takeru and Koyama, Masanori},
booktitle={The 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery \& Data Mining},
pages={2623--2631},
year={2019}
}
```

