# pykan
**Repository Path**: privateos/pykan
## Basic Information
- **Project Name**: pykan
- **Description**: No description available
- **Primary Language**: Unknown
- **License**: MIT
- **Default Branch**: master
- **Homepage**: None
- **GVP Project**: No
## Statistics
- **Stars**: 0
- **Forks**: 0
- **Created**: 2024-05-02
- **Last Updated**: 2024-05-02
## Categories & Tags
**Categories**: Uncategorized
**Tags**: None
## README
 # Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs)
This is the github repo for the paper ["KAN: Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks"](https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.19756). Find the documentation [here](https://kindxiaoming.github.io/pykan/).
Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs) are promising alternatives of Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLPs). KANs have strong mathematical foundations just like MLPs: MLPs are based on the universal approximation theorem, while KANs are based on Kolmogorov-Arnold representation theorem. KANs and MLPs are dual: KANs have activation functions on edges, while MLPs have activation functions on nodes. This simple change makes KANs better (sometimes much better!) than MLPs in terms of both model **accuracy** and **interpretability**. A quick intro of KANs [here](https://kindxiaoming.github.io/pykan/intro.html).
# Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs)
This is the github repo for the paper ["KAN: Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks"](https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.19756). Find the documentation [here](https://kindxiaoming.github.io/pykan/).
Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs) are promising alternatives of Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLPs). KANs have strong mathematical foundations just like MLPs: MLPs are based on the universal approximation theorem, while KANs are based on Kolmogorov-Arnold representation theorem. KANs and MLPs are dual: KANs have activation functions on edges, while MLPs have activation functions on nodes. This simple change makes KANs better (sometimes much better!) than MLPs in terms of both model **accuracy** and **interpretability**. A quick intro of KANs [here](https://kindxiaoming.github.io/pykan/intro.html).
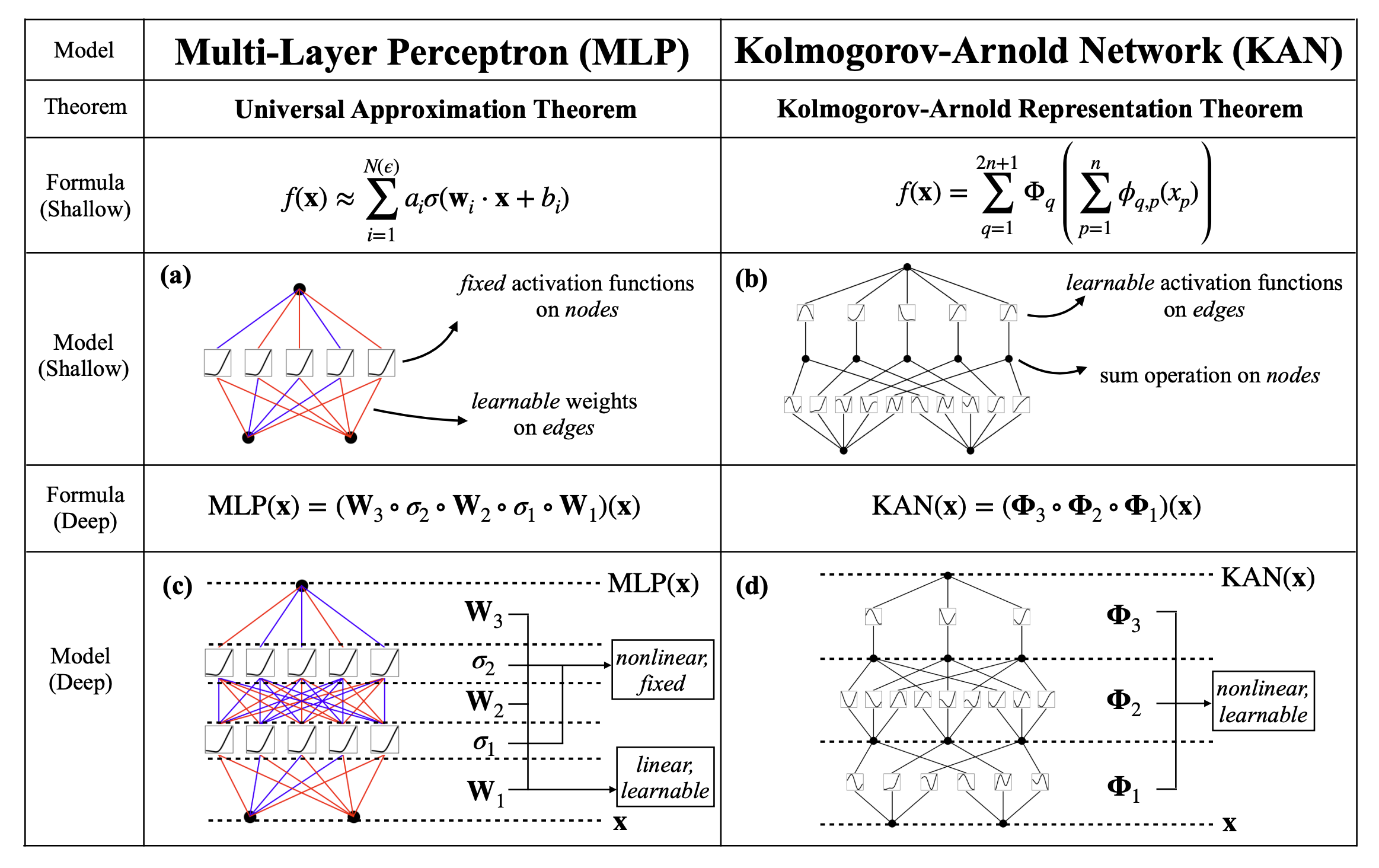 ## Accuracy
**KANs have faster scaling than MLPs. KANs have better accuracy than MLPs with fewer parameters.**
**Example 1: fitting symbolic formulas**
## Accuracy
**KANs have faster scaling than MLPs. KANs have better accuracy than MLPs with fewer parameters.**
**Example 1: fitting symbolic formulas**
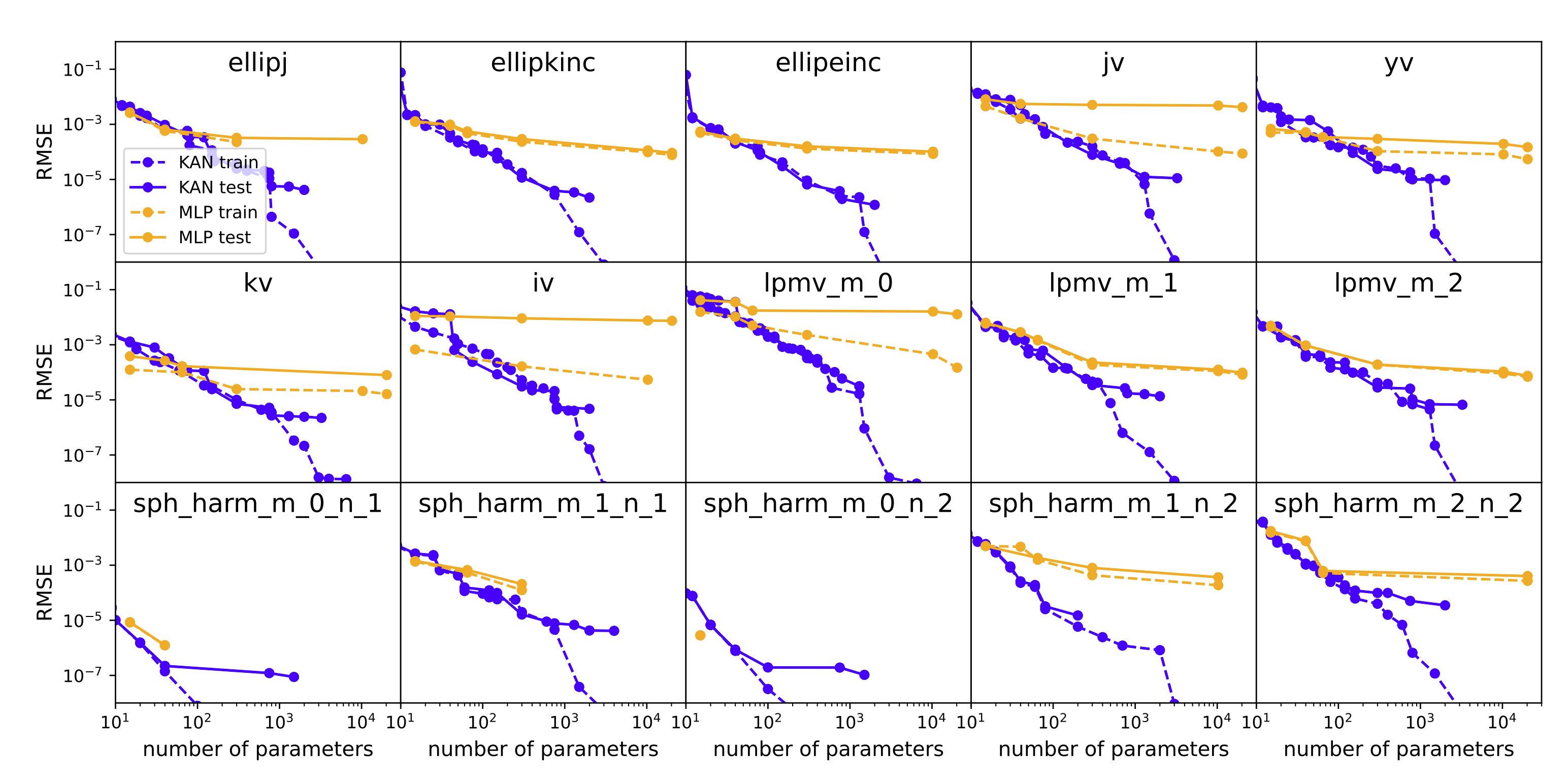
 **Example 2: fitting special functions**
**Example 2: fitting special functions**
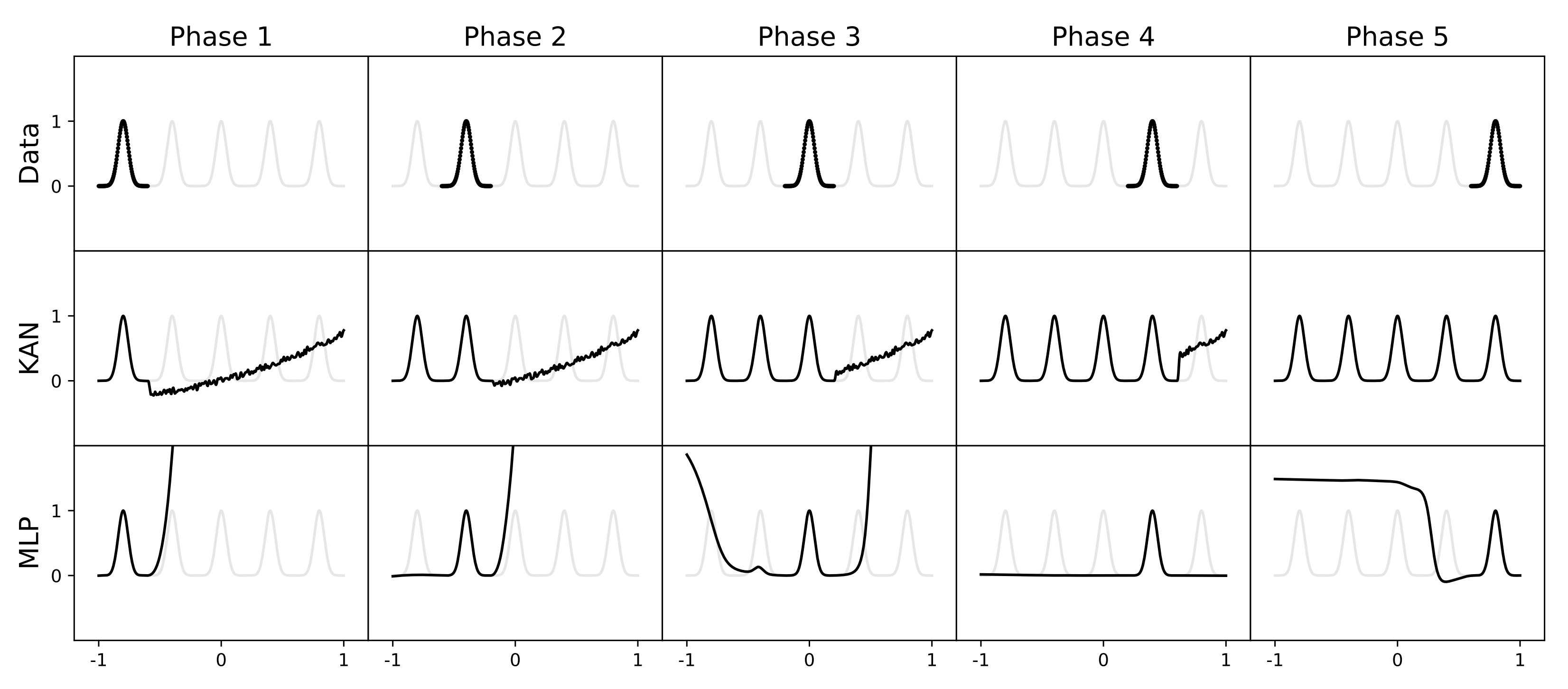
 **Example 3: PDE solving**
**Example 3: PDE solving**
 **Example 4: avoid catastrophic forgetting**
**Example 4: avoid catastrophic forgetting**
 ## Interpretability
**KANs can be intuitively visualized. KANs offer interpretability and interactivity that MLPs cannot provide. We can use KANs to potentially discover new scientific laws.**
**Example 1: Symbolic formulas**
## Interpretability
**KANs can be intuitively visualized. KANs offer interpretability and interactivity that MLPs cannot provide. We can use KANs to potentially discover new scientific laws.**
**Example 1: Symbolic formulas**
 **Example 2: Discovering mathematical laws of knots**
**Example 2: Discovering mathematical laws of knots**
 **Example 3: Discovering physical laws of Anderson localization**
**Example 3: Discovering physical laws of Anderson localization**
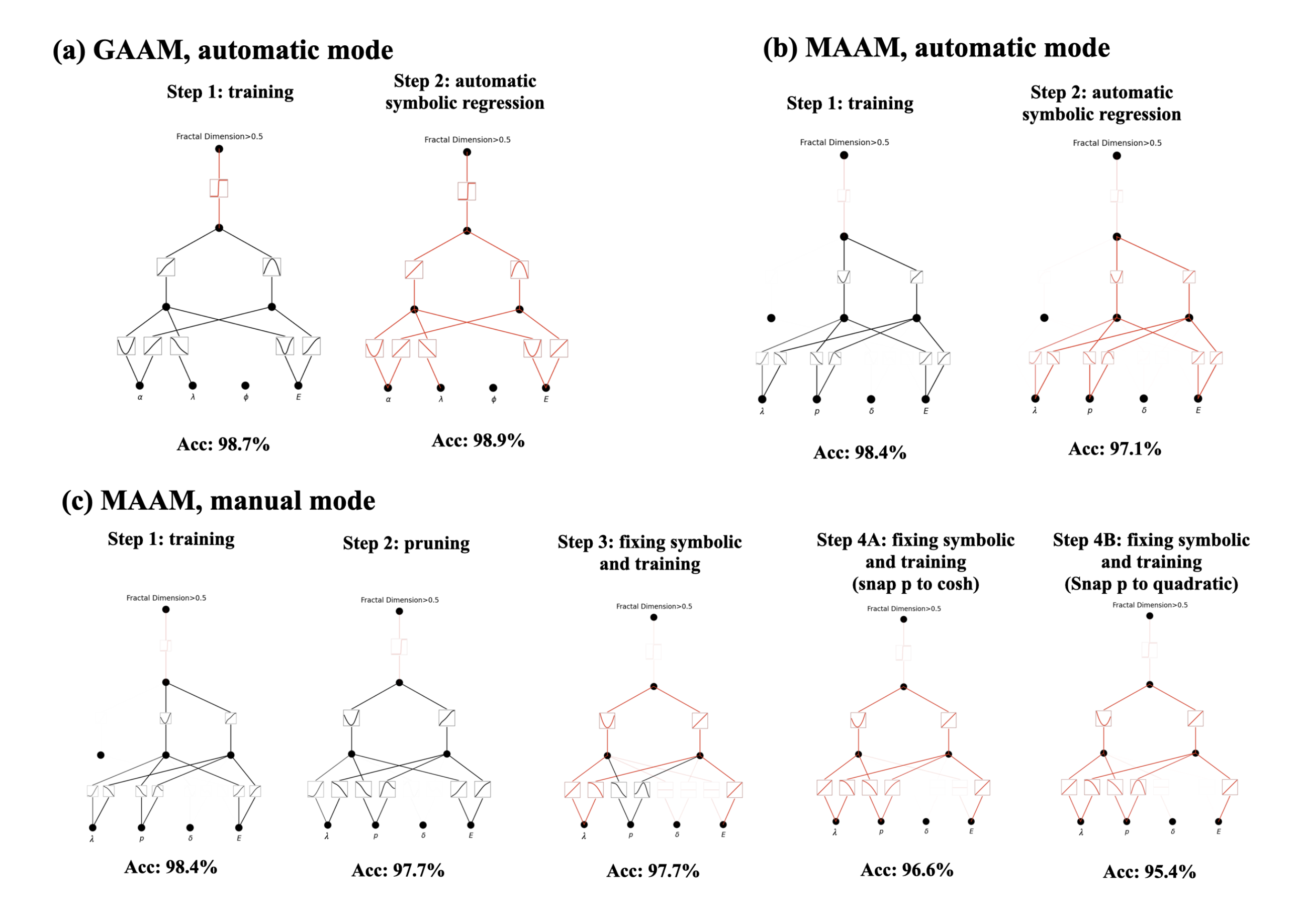 **Example 4: Training of a three-layer KAN**

## Installation
There are two ways to install pykan, through pypi or github.
**Installation via github**
```python
git clone https://github.com/KindXiaoming/pykan.git
cd pykan
pip install -e .
```
**Installation via pypi**
```python
pip install pykan
```
Requirements
```python
# python==3.9.7
matplotlib==3.6.2
numpy==1.24.4
scikit_learn==1.1.3
setuptools==65.5.0
sympy==1.11.1
torch==2.2.2
tqdm==4.66.2
```
To install requirements:
```python
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Computation requirements
Examples in [tutorials](tutorials) are runnable on a single CPU typically less than 10 minutes. All examples in the paper are runnable on a single CPU in less than one day. Training KANs for PDE is the most expensive and may take hours to days on a single CPU. We use CPUs to train our models because we carried out parameter sweeps (both for MLPs and KANs) to obtain Pareto Frontiers. There are thousands of small models which is why we use CPUs rather than GPUs. Admittedly, our problem scales are smaller than typical machine learning tasks, but are typical for science-related tasks. In case the scale of your task is large, it is advisable to use GPUs.
## Documentation
The documentation can be found [here](https://kindxiaoming.github.io/pykan/).
## Tutorials
**Quickstart**
Get started with [hellokan.ipynb](./hellokan.ipynb) notebook.
**More demos**
More Notebook tutorials can be found in [tutorials](tutorials).
## Citation
```python
@misc{liu2024kan,
title={KAN: Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks},
author={Ziming Liu and Yixuan Wang and Sachin Vaidya and Fabian Ruehle and James Halverson and Marin Soljačić and Thomas Y. Hou and Max Tegmark},
year={2024},
eprint={2404.19756},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.LG}
}
```
## Contact
If you have any questions, please contact zmliu@mit.edu
**Example 4: Training of a three-layer KAN**

## Installation
There are two ways to install pykan, through pypi or github.
**Installation via github**
```python
git clone https://github.com/KindXiaoming/pykan.git
cd pykan
pip install -e .
```
**Installation via pypi**
```python
pip install pykan
```
Requirements
```python
# python==3.9.7
matplotlib==3.6.2
numpy==1.24.4
scikit_learn==1.1.3
setuptools==65.5.0
sympy==1.11.1
torch==2.2.2
tqdm==4.66.2
```
To install requirements:
```python
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Computation requirements
Examples in [tutorials](tutorials) are runnable on a single CPU typically less than 10 minutes. All examples in the paper are runnable on a single CPU in less than one day. Training KANs for PDE is the most expensive and may take hours to days on a single CPU. We use CPUs to train our models because we carried out parameter sweeps (both for MLPs and KANs) to obtain Pareto Frontiers. There are thousands of small models which is why we use CPUs rather than GPUs. Admittedly, our problem scales are smaller than typical machine learning tasks, but are typical for science-related tasks. In case the scale of your task is large, it is advisable to use GPUs.
## Documentation
The documentation can be found [here](https://kindxiaoming.github.io/pykan/).
## Tutorials
**Quickstart**
Get started with [hellokan.ipynb](./hellokan.ipynb) notebook.
**More demos**
More Notebook tutorials can be found in [tutorials](tutorials).
## Citation
```python
@misc{liu2024kan,
title={KAN: Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks},
author={Ziming Liu and Yixuan Wang and Sachin Vaidya and Fabian Ruehle and James Halverson and Marin Soljačić and Thomas Y. Hou and Max Tegmark},
year={2024},
eprint={2404.19756},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.LG}
}
```
## Contact
If you have any questions, please contact zmliu@mit.edu